Global enterprises now operate across markets, languages, and cultural contexts simultaneously. Translations now directly influence market expansion, customer trust, and brand perception.
Traditional translation workflow is no longer adequate to handle the scale and speed of this shifting global ecosystem. This is where AI-driven translation workflows have started to shine.
Today, the market for AI translation services has reached $2.65 billion and is growing at 22.6% annually.
This article explains how AI for translation is reshaping the translation industry through hybridized workflows, how these workflows function, how to evaluate translation quality using quantifiable metrics, and how organizations can calculate ROI when adopting AI-augmented translation pipelines.
What is AI for Translation?
AI for translation refers to translation workflows where AI systems, such as neural networks and machine learning algorithms, generate or assist with translation output.
Now, it’s important to note that enterprise-grade translation workflows are vastly different from your average Google or other web-based translation services. They’re much more advanced than the consumer-grade Machine Translations, even.
Here are the key distinctions between various AI translators and their use cases, summarized with a simple table:
| Model | Description | Best Use Case |
| Machine Translation (MT) | Statistical or neural models that translate based on learned patterns. | High-volume but low-stakes text. |
| AI-Assisted / Human-in-the-Loop Translation | AI generates initial output; linguists refine tone, terminology, and nuance. | Marketing, HR, product copy, and regulated content. |
| AI-Enhanced Localization | AI integrated across the full translation management system (TMS): glossary consistency, quality scoring, and formatting validation. | Enterprise localization at scale. |
Neural Machine Translators handle the bulk of today’s workflow, as LLMs get increasingly fine-tuned to suit multilingual ecosystems.
How AI Translation Works: From Model Training to Output
The act of translating words into another language may seem simple on the surface, but it is a complex and intricate process that requires sophisticated machinery.
Here’s a simplified 5-step process that outlines the core workflow in its most essential form:
1. Data Preparation & Model Training
AI translation models begin their journey with extensive data preparation, which involves processes like training on parallel bilingual corpora and domain-specific glossaries. This is to ensure the model understands both general language and specialized terminology.
Tokenization, which is the process of converting text into sub-word units for processing, is then applied. This enables the model to process language at a granular level.
Linguistic units that correlate across languages are taught to enable the model to capture patterns in syntax, semantics, and idiomatic usage. This stage lays the foundation for accurate, context-aware translation.
2. Transformer Architecture (Plain Explanation)
Modern AI translation systems rely on transformer-based architectures, which have revolutionized language processing. These models:
- Encode meaning from the source language, capturing context, structure, and nuance.
- Decode meaning into the target language, generating fluent and coherent translations.
- Apply contextual attention, allowing the system to track dependencies across sentences and paragraphs, reducing common errors in grammar, gender agreement, and phrase continuity.
Transformers are particularly effective because they can handle long-range dependencies, making translations more natural and contextually accurate.
3. Draft Output
Once trained, the AI system generates translations at scale, rapidly processing large volumes of content.
This is where speed and cost efficiency converge, especially for enterprises managing multilingual content pipelines.
4. Human Review (Post-Editing)
Draft outputs have gotten very accurate over the years, but a human inspection is still necessary. Especially so if there are sensitive documents involved that could prove liability and or trust risks.
Post-editing ensures:
- Correct tone and audience targeting
- Consistent use of industry-specific terminology
- Preservation of cultural nuance
- Mitigation of legal or regulatory compliance risks
This step is essentially the MTPE (Machine Translation Post-Editing) process of the workflow.
5. Quality Assurance & Delivery
The final stage combines automated quality assurance checks with human sign-off, ensuring translations meet the standards.
Common evaluation metrics used include:
- BLEU – measures overlap between machine translation and reference text.
- COMET – uses neural models to estimate translation quality more contextually.
- BERTScore – compares embeddings to capture semantic similarity beyond exact word matches.
This dual-layer QA keeps the consistency of the brand value in check, all while providing confidence in the output.
What’s the Difference Between AI and Machine Translation?
Machine and AI translations are often used interchangeably. But they are not quite the same in a broader sense, one may think, despite a machine doing the bulk of the work in most cases.
Let’s look into it.
Machine Translation:
IT is the earliest form of machine-assisted translation, and relied heavily on algorithms for the translation process. This is ideal for translating quickly and in large volumes. However, it lacks the cultural contexts and nuances of a language and is best suited for literal translations.
Google Translate and Microsoft Translator are some of the most popular examples of this technology.
AI Translation:
While early experiments in AI translation began in the 1950s, the technology as we know it today was born with the advent of Neural Machine Translation (NMT) around 2015–16. Then the LLMs(Large Language Models) came and revolutionized the field.
As the name suggests, AI translation uses neural pathways and LLMs instead of statistical models like its predecessor and understands the essence and the nuances of a language instead of just putting out words.
One of the most popular examples of AI translation is ChatGPT.
What Are AI Translation Workflows in Modern Localization Pipelines?
A modern enterprise translation workflow nowadays is an amalgamation of AI translation tools with human ingenuity. This way, the translations get done fast, and a last minute human signoff ensures the quality and integrity of the AI language translations.
This lifecycle typically looks a little something like this: ingestion → pre-processing → MT → MTPE → LQA → delivery
Here’s a more in-depth discussion:
Content Ingestion: (CMS, API, TMS integration)
Source content is automatically pulled from content management systems (CMS), translation management systems (TMS), or via APIs. This integration ensures continuous localization. Every new cycle, webpage, or document enters the translation pipeline in real time.
Pre-Processing: (cleanup, terminology matching, segmentation)
Before translation, the content undergoes a few preparatory processes, such as;
- text cleanup (removing formatting noise or code)
- terminology alignment (matching with approved termbases)
- segmentation (dividing text into manageable translation units)
These steps prepare data for consistent, high-quality translation.
AI Draft Translation: (NMT / LLM)
This stage uses Neural Machine Translation (NMT) or Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate initial translations. The system leverages context-aware algorithms to produce fluent, near-human text at scale.
AI translation drastically reduces turnaround times and costs while maintaining acceptable quality for most content types.
Human Post-Editing (PE or MTPE)
With the evolution of LLMs, AI language translations are becoming near-human texts. However, a human oversight is still necessary.
In this step, linguists fix the tone, terminology, and cultural nuances to ensure the translation aligns with brand voice and local market expectations
Linguistic Quality Assurance (LQA)
After post-editing, translations undergo linguistic QA checks.
This step is a mix of automated tools and another round of human review to catch any remaining errors in grammar, consistency, or formatting. It guarantees compliance with client style guides and quality benchmarks such as BLEU, COMET, or BERTScore.
Formatting, Compliance, Delivery
The finalized translations are formatted, localized (dates, currencies, layouts), and checked for regulatory and or accessibility compliance.
They’re then delivered to the target systems or published.
Feedback Loop for Continuous Model Improvement
Post-project feedback, reviewer comments, and updated glossaries are fed back into the system to fine-tune AI models and improve performance over time.
This is not necessarily a part of the workflow. But it is crucial for the development of the AI translation systems, and helps enterprises achieve better accuracy and faster turnaround with every iteration.
Hybrid Human + AI Workflows for Accuracy & Speed
This hybrid process, mostly known as MTPE, is a very efficient system that allocates the resources properly and speeds up the production.
Works that are non-essential and require little adjustment are done using AI translation systems with little to no human intervention.
And if there’s liability at stake, then more powerful and precise measures are taken during the AI translations, and multiple rounds of LQA are done to ensure it checks all the boxes.
This bi-layered approach cuts edit time by 80%. [source: languageline.com]
Where AI Fits in the Translation Supply Chain
AI support is used throughout the entire cycle of the translation process. Here’s a table that summarizes this quickly:
| Task | AI’s Contribution |
| Glossary Management | Suggests term usage consistency across documents |
| Quality Estimation (QE) | Predicts which segments require human editing |
| Project Effort Estimation | Forecasts translation time + cost before work begins |
| Translation Memory (TM) Optimization | Learns from previously approved translations |
How to Measure Translation Quality in AI-Driven Projects
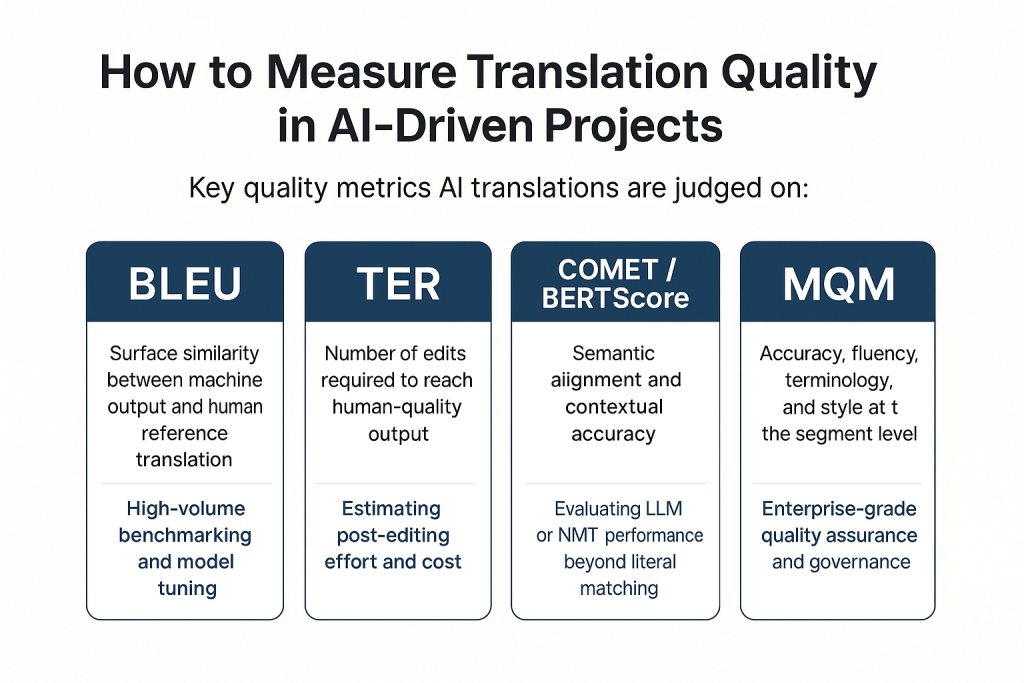
Evaluations in AI translation are very strict and adhere to an industry standard. However, they do vary across projects and requirements, and quantitative evaluations are often hard to get.
AI translation technologies, maybe cheap and convenient, but they’re still far from being totally self-reliant, and a human insight is still required. Modern enterprises use a combination of automated model metrics and human-centered frameworks to ensure translations meet both linguistic and business standards.
AI Translation Quality Metrics Explained
Below are the key quality metrics AI translations are judged on;
| Metric | Measures | Best For |
| BLEU | Surface similarity between machine output and human reference translation | High-volume benchmarking and model tuning |
| TER (Translation Edit Rate) | Number of edits required to reach human-quality output | Estimating post-editing effort and cost |
| COMET / BERTScore | Semantic alignment and contextual accuracy | Evaluating LLM or NMT performance beyond literal matching |
| MQM (Multidimensional Quality Metrics) | Accuracy, fluency, terminology, and style at the segment level | Enterprise-grade quality assurance and governance |
| DQF (Dynamic Quality Framework) | Weighted quality scores linked to business KPIs | Tracking vendor performance and workflow optimization |
Top AI translation services like Circle Translations rely on these metrics and set appropriate exceptions based on them.
Human Evaluation: Why the Final Review Still Matters
AI translation tools are great for bulkier projects, but there are often mistakes made, contexts get overlooked, and nuances are lost. Linguistic QAs are there to solve this very problem. These works go through several rounds of QA based on the severity of the project.
Human Evaluation is thus crucial to preserve nuances across multiple languages and the brand voice across multiple content pipelines.
Calculating ROI for AI Translation in B2B Workflows
ROI=(Cost Savings+ Time Savings+ Quality Gains)Investment
The formula states a clear relation among ROI, cost savings, and time savings. AI translations’ biggest advantage is to drastically reduce both of these.
Here’s a business scenario example
company translating product documentation across 12 languages:
| Approach | Cost per Word | Total Words | Annual Total |
| Human-only | €0.12 | 2,000,000 | €240,000 |
| Hybrid AI + Human | €0.07 | 2,000,000 | €140,000 |
Annual Savings: €100,000
Time-to-Market Acceleration: 30–50% faster launch cycles
Quality Gains: Higher TM reuse + fewer revision cycles
How AI Reduces Translation Costs Without Compromising Accuracy
AI processes reduce the turnaround rate drastically, resulting in faster delivery cycles, lower operational costs, and improved scalability across global markets. Enterprises adopting MTPE (Machine Translation + Post-Editing) workflows typically report 30–50% lower translation expenses compared to fully human workflows.
This increase in efficiency is not without errors; therefore, linguists don’t have to waste time fixing mistakes and can focus on cultural contexts and nuances.
Productivity & Time-to-Market Benefits
AI translation drives significant productivity and accelerates time-to-market. Enterprises like Circle Translations scale efficiently across 120+ languages, prepare content for global audiences faster than ever.
This capability has a direct impact on multiregional launch speed, enabling simultaneous product releases and marketing campaigns across multiple markets.
Risks, Limitations & Best Practices in AI Translation
Although AI translation can be a great assistive tool, there are still limitations, such as hallucinations and biases. These can introduce inaccurate or misleading content, biased training data can affect fairness or tone, and regulatory concerns such as GDPR or intellectual property compliance must be carefully managed.
Where AI Translation Still Falls Short
AI tools are unmatched when it comes to speed and efficiency. But in some areas, AI translations still fall short. Such as:
- Cultural idioms
- Humor and emotional tone
- Highly specialized legal or medical terminology
- Regions with sensitive linguistic nuance
Best Practices to Combine AI Speed with Human Quality
Human oversight remedies this situation, and that is still cheaper and faster than a full-scale human-only operation.
Here’s the 3-tier QA model that is industry standard: AI pre-pass → Human edit → LQA metric scoring
Why Choose Circle Translations for AI-Enhanced Workflows

At Circle Translations, we integrate AI into your localization value chain, extending its benefits beyond simple applications.
Our AI-driven translation workflows combine human linguistic expertise, secure infrastructure, and enterprise-grade automation to deliver accuracy, speed, and quantifiable business impact.
What Sets Us Apart
Native, Domain-Specialized Linguists
We work with certified translators and subject-matter experts across 120+ languages and 124+ language pairs.
Whether your content is technical, financial, legal, or marketing-focused, every linguist refines AI-generated drafts for cultural nuance and compliance, ensuring enterprise-ready accuracy.
ISO-Aligned Quality Frameworks
All AI-assisted projects follow MQM/DQF and COMET quality metrics to objectively measure performance.
Each translation undergoes human review, LQA scoring, and BLEU benchmarking, turning linguistic quality into data-backed insight. Second-linguist reviews are standard in our Business and Pro tiers, reducing error propagation across projects.
Hybrid AI + Human Post-Editing Workflows
Our workflows blend Neural and LLM translation with human-in-the-loop (HITL) validation. AI accelerates content throughput by up to 70%, while post-editing ensures tone, intent, and brand voice remain precise.
This model consistently delivers 30–50% cost savings without compromising quality or regulatory integrity.
24/7 Project Management & Global Coverage
Our dedicated PMs and linguist teams operate on a follow-the-sun model, providing real-time updates across time zones.
For enterprises managing global product releases, this means no downtime, no missed deadlines, and transparent communication at every milestone.
Secure, Compliant, and Confidential
Every file is processed within encrypted, NDA-backed, GDPR-compliant environments. Circle Translations offers SOC-style security documentation upon request for regulated industries, including Finance, Healthcare, and Legal.
Your content, and its underlying data, are never reused or stored beyond project scope.
Flexible AI-Enhanced Service Tiers
Choose from Basic, Business, Pro, or Custom plans to align translation depth and speed with project scale.
Each tier supports AI-assisted translation, human review, and quality benchmarking, giving you full visibility into cost savings, accuracy scores, and turnaround metrics.
Integration-Ready Localization
Our workflows integrate with modern content ecosystems, CMS, Git, Figma, JSON/PO, API-based TMS connectors, ensuring seamless translation pipelines without disrupting your development or publishing flow.
How We Drive ROI Beyond Translation Cost
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: AI + human workflows reduce turnaround by up to 70%, enabling simultaneous multilingual launches.
- Consistent Brand Voice: Style guides, termbases, and translation memory ensure cross-market uniformity and stronger brand trust.
- Lower QA Overhead: Automated LQA metrics identify issues early, cutting human review cycles by 30–40%.
- Data Transparency: You receive detailed reports on BLEU, COMET, and MQM scores, showing exactly where efficiency gains occur.
Summary
AI translation has revolutionized the industry with cutting-edge efficiency and accuracy that a human-only production simply can’t compare. However, there are still shortcomings of AI tools as well. AI still struggles with nuances across multiple languages; thus, human oversight is still a necessity.
For enterprises, the key takeaway is balance. AI delivers scalability, cost reduction, and speed, while human linguists ensure accuracy, cultural nuance, and compliance. When orchestrated through a structured workflow, content ingestion, AI draft, post-editing, and LQA, organizations gain up to 50% lower translation costs and 70% faster turnaround, all while maintaining brand integrity.
AI translation is no longer experimental–it’s operational, measurable, and secure. Enterprises across the markets are using the features with varying levels of human oversight, resulting in increasing ROI with very low turnaround time.
Frequently Asked Questions
How accurate is AI translation for business content?
Modern AI translation achieves 80–95 % accuracy when paired with human post-editing. Neural and LLM-based systems deliver strong consistency, but human linguists remain vital for tone and context.
At Circle Translations, each AI-generated draft undergoes LQA and SME review, ensuring cultural precision and brand alignment, trusted by enterprise clients
How does AI translation improve ROI for enterprises?
AI translation cuts costs by 30–50 % and boosts turnaround speed by 40–70 % compared to manual workflows. ROI is tracked through lower per-word pricing, faster global rollout across multilingual markets, and adaptive learning that continually enhances quality.
Can AI handle industry-specific jargon (finance, legal, healthcare)?
In short, yes.
With domain-tuned models and human SME review. AI ensures speed and consistency, while expert linguists validate complex terminology.
Is AI translation secure for confidential documents?
If handled within a secure, GDPR-compliant environment, yes, AI translation can absolutely be secure for sensitive files.
What are the best AI translation tools for enterprises?
Leading solutions include DeepL, Lilt, Lokalise AI, Amazon Translate, and Azure AI Translation.
Circle Translations employs a multi-engine architecture, integrating these tools within its proprietary post-editing and QA systems to deliver optimal accuracy and scalability for every domain.
Should I use AI-only translation for critical documents?
AI-only translation can miss nuance, tone, or legal phrasing. So, no; using AI-only translation is not advisable.