If you’re a hospital administrator or healthcare product company evaluating translation budgets, you’ve likely discovered that medical translation services cost significantly more than general business translation.
A patient communication document priced at standard rates suddenly becomes subject to compliance reviews and specialized terminology costs. A clinical trial instruction file requires certified medical translations and SME review. A device labeling update carries regulatory implications that affect pricing and turnaround time.
Understanding what drives these costs allows you to budget accurately, request realistic quotes, and evaluate whether you’re getting appropriate quality for your investment.
This guide provides a detailed breakdown of medical translation pricing, explains key cost drivers, and offers practical strategies for controlling costs without compromising accuracy or compliance.
What Drives Medical Translation Services Cost in 2025?
Medical translation rates are determined by multiple interconnected factors that compound to affect final pricing.
Language pair, Specialization within medical translation, Certification and regulatory requirements, Regulatory environment, File type and formatting, and Turnaround speed add layers of complexity, and a lack of availability that drives the cost way higher than a general business translation. Medical translation costs vary by language pair, specialization, certification, compliance, format, and turnaround time. Common language pairs benefit from larger talent pools and lower rates, while specialized fields, certified or notarized translations, and regulated environments (HIPAA, FDA, GDPR) increase cost. Complex file formats and urgent delivery further raise pricing due to added QA, DTP, and rush resource requirements.
Medical Translation Pricing by Language Pair
Healthcare translation costs vary significantly based on language combination and market regulatory complexity.
For instance, English to Spanish or French medical translation benefits from abundant qualified translators and established healthcare frameworks. However, regional variations matter, such as for Spanish, Mexico, Colombia, and Spain, and for French, France, Canada, and Africa, each have distinct medical terminology and regulatory environments.
English-to-Arabic, Japanese, and Korean medical translation, on the other hand, introduces substantial cost premiums. These translations require navigating multiple regional variants and distinct healthcare regulatory frameworks, common law and civil law healthcare systems, plus extensive pharmaceutical and device terminology specific to the native markets, and involve unique regulatory requirements for device approvals and clinical trial submissions specific to native health authorities.
These higher rates reflect the scarcity of qualified healthcare specialists in these language pairs. Medical terminology is specialized, and regulatory compliance requirements in these markets demand translators with deep domain expertise, difficult to find, and command premium compensation.
Circle Translations maintains relationships with medical specialists across these regions, ensuring terminology accuracy and regulatory compliance without inflated costs.
Impact of Document Type on Medical Translation Pricing
Low-risk internal documents, such as training materials, internal newsletters, and staff communications, typically cost at the lower end of medical translation pricing ranges. These documents don’t face regulatory scrutiny or patient-safety implications, allowing less experienced translators to handle the work.
Moderate-risk documents like general patient information materials, educational content, and discharge summaries require experienced medical translators with subject-matter knowledge but don’t require specialized regulatory compliance review. These typically fall in the higher end.
Clinical trial instructions, patient consent forms, device manuals, instructions for use/IFUs, safety protocols, and medication dosage information, which are considered high-risk clinical documents, command premium rates because mistranslation directly impacts patient safety and regulatory compliance. These documents require senior medical translators, SME (subject-matter expert) review, multiple quality assurance cycles, and often certification or regulatory approval before release.
Regulated submission documents like FDA submissions, clinical trial protocols, device licensing applications, and regulatory correspondence, however, require the highest expertise and most rigorous quality assurance, often reaching $0.25–$0.50 per word depending on complexity and regulatory environment.
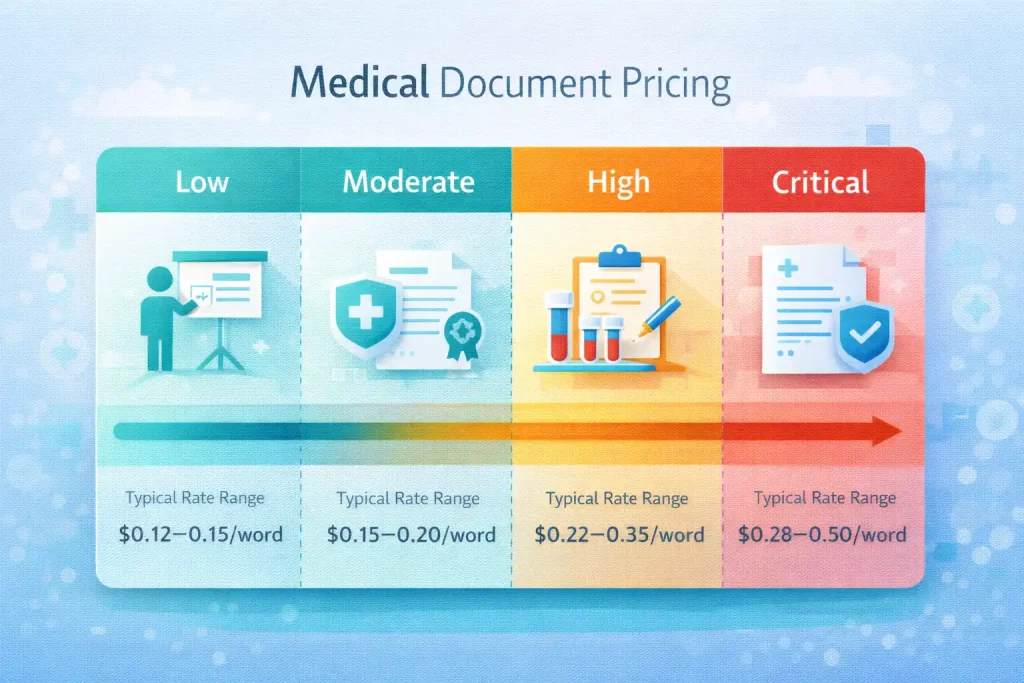
A typical risk-tier mapping illustrates the cost impact:
| Document Type | Risk Level | Typical Rate Range |
| Internal training materials | Low | $0.12–$0.15/word |
| Patient information materials | Moderate | $0.15–$0.20/word |
| Clinical trial documents | High | $0.22–$0.35/word |
| FDA/regulatory submissions | Critical | $0.28–$0.50/word |
| Certified/notarized documents | Certified | $30–$80/page |
Why Regulated Healthcare Content Costs More to Translate
The higher cost of translating regulated medical content isn’t just about profit margins. It takes real work and real risk management.
Terminology accuracy requirements are non-negotiable. A single mistranslated medical term can trigger clinical errors, regulatory rejection, or patient harm. Medical translators must research terminology extensively, verify definitions across multiple regulatory systems, and ensure consistency throughout documents. This research time adds measurable cost to medical translation pricing.
Reviewer sign-off and compliance review are mandatory in medical translations. Regulated medical documents typically undergo sign-off by qualified reviewers who verify regulatory compliance, terminology accuracy, and alignment with target-market standards. This review layer is built into medical translation pricing because it’s legally required, and not optional.
SME (subject-matter expert) linguists command higher rates than general translators. An oncology specialist translator with deep pharmaceutical knowledge costs more than a general translator. That expertise premium reflects years of specialized education and experience.
Revision and quality assurance cycles are more extensive for regulated content. While general translation might have one review layer, regulated medical translation typically includes multiple QA steps: translator review, SME review, compliance review, and final sign-off. Each cycle requires skilled linguists and adds cost, but each step measurably reduces the risk of costly downstream problems.
Circle Translations approaches medical translation with this framework: cost is connected to risk mitigation, not inflated pricing. Higher regulatory stakes justify more rigorous processes, and those processes cost more because they prevent far costlier problems.
Medical Translation Pricing Models Explained
Healthcare translation costs vary based on how work is billed, the level of certification required, and how quickly the content must be delivered. Some pricing models scale with document length, while others reflect fixed administrative and compliance responsibilities. Additional requirements, such as legal validation, regulatory acceptance, or extended quality review, naturally add complexity and cost.
Understanding how healthcare translation is billed helps you budget accurately and compare quotes effectively.
Per-Word vs Per-Page vs Hourly: Which Model Fits Your Content?
Per-word pricing: This applies to most healthcare documents like research papers, clinical documentation, patient information materials, and compliance writing. A vendor quotes a per-word rate, you provide the word count, and the invoice equals words × rate. This model scales naturally with document length.
Per-page pricing: applies to certified affidavits, regulatory submissions, notarized translations, and device labels. Per-page rates vary depending on language pair, document type, and certification level, and account for the fixed administrative overhead of authentication, formatting, and regulatory compliance.
Hourly or project fees: When healthcare translation includes research, terminology cleanup, quality assurance cycles, glossary building, or multiple revision rounds, hourly or project-based pricing makes the most sense. A project involving terminology standardization across a 50-page regulatory submission might be quoted as a fixed project fee rather than per-word rates, because the scope extends beyond linear translation work.
Certified, Sworn & Notarized Medical Translation Pricing
Certification adds measurable cost because of administrative overhead and legal liability. Certified medical translation costs vary greatly depending on language pair and certification type. The cost of translator signature, official seal, regulatory-compliant formatting, and often court registration or notary involvement also influences the cost further, with different regions charging different rates.
Notarized medical translations, executed before a notary public, typically cost toward the higher end of this range because they require third-party official involvement and often multiple certified copies.
Sworn medical translations are required in certain jurisdictions for legal proceedings, immigration applications, or device regulatory submissions, and typically cost the most because they involve court-authorized translators and official oaths.
“When is certification required?”
Clinical trial regulatory submissions, device licensing approvals, import/export documentation, litigation records, and certain FDA submissions typically require certified or sworn translations. Know your requirements before requesting quotes, as certification dramatically affects cost.
Rush vs Standard Delivery Cost Differences
Standard healthcare translation timelines allow for full quality assurance cycles, which are typically 5–10 business days for complex documents. Urgent timelines compress these cycles and increase cost.
20–30% rush premium is an industry standard for moderately accelerated timelines, 3–5 business days. This reflects the cost of pulling translators from other projects and compressing quality assurance.
Some providers charge 40%+ rush premium for expedited timelines (24–48 hours). This reflects significant resource mobilization, overtime compensation, and parallel QA workflows instead of sequential review.
Cost Control Without Sacrificing Accuracy or Compliance
Several practical strategies reduce medical translation costs while maintaining quality and regulatory compliance.
Translation memory and glossary management are key feature translation agencies use to keep prices low. This lowers the cost through repetition discounts. If you translate regularly, building a shared translation memory (TM) and medical terminology glossary means repeating terms, phrases, and concepts, translating faster and more consistently on subsequent projects. After initial investment in glossary building, projects cost less per word because translators spend less time on research. Circle Translations maintains client-specific TMs and glossaries, ensuring consistency and cost-efficiency across your entire medical translation program.
Correct source formatting reduces translation scope. Provide clean, well-organized source files rather than scanned PDFs, poorly formatted documents, or mixed-media files. Translators spend less time on document cleanup, reducing per-word costs.
Batch similar documents together. If you have multiple patient information sheets, several device manuals, or a series of training documents, translate them together. Translators build terminology familiarity, reuse glossaries, and work more efficiently when translating similar content in sequence. Batching can reduce per-project costs 10–15% compared to translating documents individually.
Avoid last-minute rushes. Plan multilingual timelines well in advance. Medical translation timelines are longer than general translation because they need to clear multiple regulatory reviews and compliance verifications across multiple jurisdictions. Building these timelines into your project planning eliminates rush premiums.
Use consistent vendors. Switching between translation providers for different medical translation projects increases onboarding time and reduces vendor familiarity with your terminology, regulatory environment, and quality standards. A consistent vendor relationship builds efficiency and may qualify you for volume discounts. Circle Translations offers retainer models for healthcare organizations with ongoing translation needs, providing discounted rates in exchange for committed monthly volume.
Who Should Handle Medical Translation: Freelancer vs Agency?
This question hinges on risk tolerance, compliance requirements, and scale.
Freelance medical translators: They provide cost-effective translation for lower-risk internal documents or non-regulated content. However, freelancers typically lack the infrastructure for certified translations, compliance review, and vendor accountability.
Translation agencies: Agencies provide oversight, compliance frameworks, vendor accountability, and access to SME reviewers. Agencies maintain errors-and-omissions insurance, HIPAA-compliant workflows, NDA processes, and quality assurance protocols. For any regulated medical translation, an agency provides liability protection and compliance assurance that freelancers cannot.
Circle Translations operates as a full-service healthcare translation agency. We maintain HIPAA-compliant workflows, ISO 17100 quality standards, SME linguist networks, and vendor accountability. For healthcare providers translating regulated content. Clinical trials, device approvals, regulatory submissions, and agency infrastructure are areas where risk management is essential. Circle Translations understands and assumes this responsibility, applying rigorous quality controls, subject-matter expertise, and compliance-ready workflows at every stage.
Vendor Selection Checklist for Healthcare Providers
When evaluating medical translation vendors, use this procurement checklist:
- ISO 17100 certification or equivalent quality standard alignment
- HIPAA familiarity and compliance workflow confirmation
- Revision policy: How many revision rounds are included before additional charges apply?
- NDA/PHI handling: How is sensitive healthcare data protected?
- SME availability: Can the vendor access subject-matter expert reviewers?
- Sector experience: Does the vendor have demonstrated experience in your specific healthcare specialty?
- SLA transparency: Are service level agreements and turnaround time guarantees in writing?
- Certification capabilities: Can the vendor provide certified or notarized medical translations when required?
- Technology infrastructure: Does the vendor use translation memory, terminology management tools, and quality assurance software?
This checklist separates vendors with serious healthcare translation infrastructure from those offering general translation services with healthcare positioning.
Conclusion
Medical translation services cost more than general translation because healthcare translation carries liability, regulatory complexity, and patient safety implications. Understanding cost drivers, language pair, document type, specialization, certification needs, and urgency allows you to budget accurately and select vendors who provide appropriate quality for your regulatory environment.
The cheapest medical translation is rarely the best investment. A mistranslation in a clinical trial document, device manual, or regulatory submission can trigger regulatory rejection, clinical errors, or patient harm worth far more than translation savings. Conversely, investing in qualified medical translators, certified translations where required, and rigorous quality assurance protects your organization and patients.
When evaluating medical translation quotes, focus on vendor qualifications, compliance infrastructure, and quality processes rather than per-word rates alone. A vendor charging premium rates with rigorous QA and SME review may provide better value than a vendor charging cheaper rates without compliance oversight.
At Circle Translations, we understand healthcare translation as risk management. Our medical specialists are vetted healthcare translation experts. Our quality processes include SME review, compliance verification, and terminology consistency checks. We maintain HIPAA-compliant workflows and can provide certified medical translations when regulatory requirements demand them. We’re transparent about what drives costs, so you’re never surprised by your final invoice.
Request a medical translation quote or contact our healthcare translation team to discuss your clinical trial, device documentation, or regulatory submission translation needs.
Medical Translation Services Cost — FAQs
How much do medical translation services cost per word?
Medical translation pricing varies by complexity and regulatory requirements. Circle Translations offers Basic Service from €0.05 per word (machine-aided with professional review), Business Service €0.08–€0.13 per word (intricate technical texts with manual translation), Pro Service €0.10–€0.16 per word (scientific/technical with expert native translation and unlimited revisions), and Custom Service for specialized regulatory submissions and certified medical translations. Higher tiers include more rigorous quality assurance, SME review, and compliance verification.
Why does healthcare translation cost more than general translation?
Healthcare translation requires compliance verification, terminology precision, SME review, regulated workflows, and liability management. A mistranslation in medical content can trigger clinical errors, regulatory rejection, or even patient harm, costing far beyond the translation savings. Preventive accuracy through rigorous processes is why medical translation rates are higher.
Are certified translations more expensive?
Yes. Certified medical translations include the translator’s signature, an official seal, regulatory-compliant formatting, and often notary or court registration. Certification adds measurable cost because of administrative overhead and legal liability. Many regulatory submissions, device approvals, and litigation documents require certified medical translations as a compliance mandate. Contact Circle Translations for custom pricing on certified medical translation projects.
Can machine translation reduce medical translation costs?
Only for non-regulated internal review. Machine translation is not recommended for patient-facing content, clinical trial documents, or regulatory submissions without human expert review. Circle Translations Basic Service (€0.05/word) includes machine-aided translation with professional human review, suitable for low-risk internal materials. For regulated healthcare content, Pro Service (€0.10–€0.16/word) with human expert translation is required.
How do I get an accurate medical translation quote fast?
Share your source file, specify target languages, clarify document type and certification needs, note turnaround deadline, and include sample pages if available. Attach existing glossaries or terminology guides if you have them. Complete information enables vendors to provide accurate quotes without follow-up delays. Circle Translations typically responds to healthcare translation inquiries within 24 hours.
When do I need certified medical translation?
Certified medical translations are required for regulatory submissions (FDA filings, device licensing applications), clinical trial approvals, import/export documentation, litigation records, and certain immigration health documents. Know your regulatory requirements before requesting quotes, as certification dramatically affects cost and timeline.
How can I reduce medical translation costs without lowering quality?
Plan ahead to avoid rush premiums (single most effective strategy). Build translation memories and glossaries for reuse across projects. Batch similar documents together. Provide clean source files. Use consistent vendors to benefit from familiarity and volume discounts. Tier documents by risk level so senior translators handle regulated content while routine material uses less-senior resources. These strategies reduce per-project cost while maintaining compliance and quality.