Your business is expanding internationally. But before you launch across borders, you need clarity on one critical question: How much does website translation actually cost?
This isn’t a simple one-time transaction. Website translation costs extend far beyond simple translation. It encompasses ongoing localization, technical integration, SEO optimization, content operations, and maintenance workflows. For SaaS platforms, e-commerce stores, enterprise marketing sites, legal firms, and IT service providers, the financial picture looks dramatically different depending on scale, complexity, and long-term vision.
The pricing models vary significantly across the localization industry. Some vendors charge per word. Others structure fees around project scope or monthly retainers. Variables, such as word count, CMS complexity, language pairs, update frequency, and quality assurance, compound quickly.
With this guide, you’ll understand the cost drivers that matter, the pricing mechanisms available, real-world budgeting scenarios, and how to control expenses without compromising quality.
What Determines the Cost of Website Translation?
Website translation cost isn’t fixed. It moves along multiple axes simultaneously. Understanding these cost levers is crucial for smart budgeting.
The primary cost drivers include content volume, language pairs, and regional complexity, content management system (CMS) architecture, search engine optimization (SEO) localization requirements, update frequency and content cadence, quality assurance depth, and the balance between human review and machine translation capabilities.
Website localization cost rises with each additional consideration. It’s not just translation; it’s technical infrastructure, automation, quality gates, and business continuity planning.
How Does Website Size and Content Volume Affect Pricing?
Page count is a deceptive metric. A 100-page website doesn’t equal 100 translated pages if dynamic content, conditional rendering, or personalization layers complicate the picture.
Consider what actually requires translation. Visible page content is obvious, but hidden strings consume translation budgets too: menu navigation systems, pop-up notifications, error messages, form labels, filter dropdowns, checkout flows, and progressive disclosure elements. A single ecommerce product page might contain 200+ billable words beyond the visible narrative.
E-commerce catalogs present unique challenges. Product descriptions, SKU metadata, category hierarchies, variant options, and dynamic inventory messaging multiply the scope exponentially. A retailer with 2,000 SKUs across 5 languages faces roughly 10,000 product-level translation units. Maintenance becomes continuous; product updates flow through translation workflows monthly or weekly.
A SaaS company with 500+ help articles across 8 languages accumulates massive translation debt. Updates to core documentation ripple across the entire corpus. Each major product release triggers localization sprints across all supported languages.
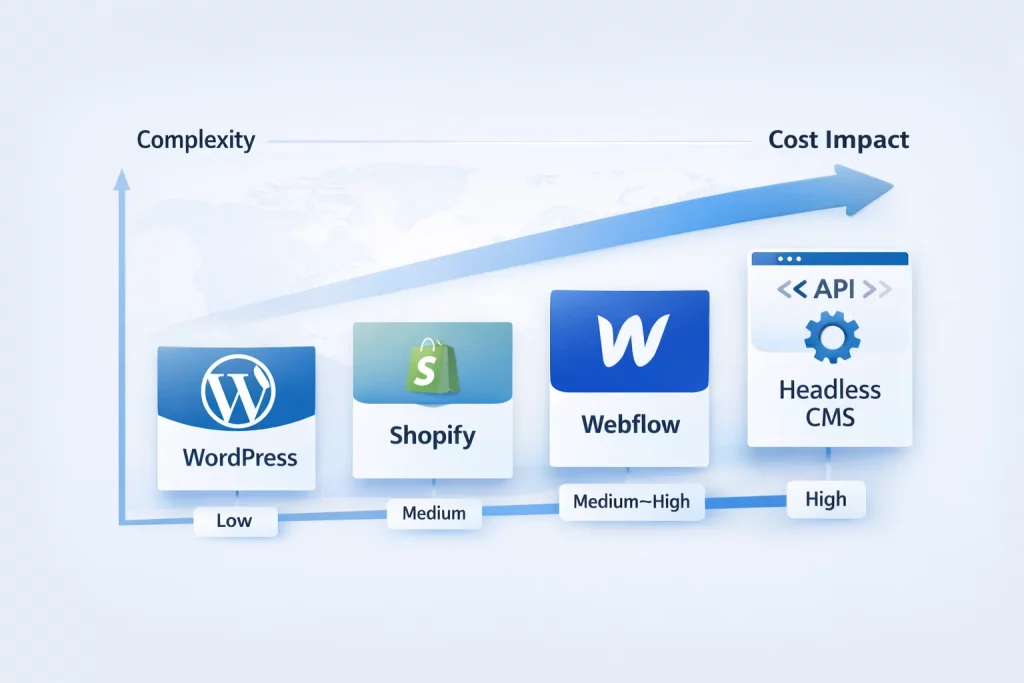
CMS complexity determines how word count translates to actual translation cost. WordPress sites with straightforward content exports are simpler to scope. Shopify stores require connector setups and string extraction. Webflow or custom-built platforms demand API integration. Some content lives in the CMS database; some is hard-coded. Some are user-generated and never stops flowing.
How Do Language Pairs and Regions Change Website Translation Costs?
The localization industry segments languages into tiers based on demand, translator availability, and linguistic complexity.
Here’s a snapshot that categorizes languages according to industry standards:
| Language Category | Examples | Translator Market | Typical Cost (per word) | Key Notes |
| High-volume European languages | English, French, German, Spanish | Large, mature translator networks | $0.08–$0.15 | Competitive pricing due to abundant native speakers |
| Regional / Central & Eastern European languages | Lithuanian, Estonian, Czech, Polish | Smaller translator pools | $0.15–$0.25 | Specialized expertise increases rates; strong fit for Baltic & Slavic specialists |
| Complex-script languages | Arabic, Chinese (Simplified & Traditional), Japanese, Korean | Limited high-skill availability | $0.20–$0.35 | Higher technical complexity (scripts, RTL, encoding, localization) |
Language-pair pricing also factors in directionality and regional locale variants. Translating from English into Arabic goes far beyond word conversion. It requires full right-to-left (RTL) layout reflow, reversed navigation logic, updated metadata, and locale-specific formatting for dates and numbers, all of which add technical complexity. Costs increase further when accounting for regional Arabic variants, such as Modern Standard Arabic versus Gulf Arabic or North African dialects, each requiring localized terminology, tone adjustments, and separate QA to ensure accuracy and cultural fit across markets.
How CMS and Platform Choice Changes Translation Cost
Your content management system architecture directly impacts the cost to translate a website. Not all CMSes are created equal from a localization perspective.
Here’s a table summarizing the industry leaders:
| Platform / System Type | Localization Complexity | Workflow Characteristics | Cost Impact | Key Considerations |
| WordPress (WPML, Polylang, etc.) | Low | Plugin-based, editor-managed translations inside WP | Low | Mature ecosystem, streamlined workflows, some plugins charge per language |
| Shopify | Medium | Native tools plus optional third-party TMS | Moderate | Rigid native system; products, metafields, and UI strings handled differently |
| Webflow | Medium–High | Page and collection duplication per language | Higher | No dynamic switching without custom code; developer involvement increases |
| Custom / Headless CMS | High | API-driven, requires string extraction and TMS integration | ~40–60% higher than traditional CMS | Heavy engineering effort; versioning, context, and sync add complexity |
| Translation Management Systems (TMS) | Enables scale | Centralized workflows, automation, translation memory | $500–3,000/month | Reduces manual work; improves consistency across many languages |
| API Integration & Sync | High (setup) | Developer-led configuration and maintenance | 40–80 dev hours upfront + ongoing | Required for automation, fallbacks, and production sync |
Website Translation Pricing Models Explained
The localization industry operates on four primary pricing structures. Most vendors combine multiple models to balance risk, predictability, and flexibility.
Per-Word Pricing for Website Content
Per-word pricing is the localization industry standard. It’s transparent, scalable, and aligns cost with actual output.
A translator analyzes your source content and assigns a per-word rate based on language pair, complexity, and volume.
But which words count as “billable”?
Billable words are the source-language words extracted from your CMS that require translation. HTML markup and code are excluded, but hard-coded user-facing strings are included. Repeated content may be discounted through translation memory, and final costs can be affected by language expansion or compression.
Website translation cost per word varies wildly across vendors and languages. Here’s Circle Translations’ pricing tiers, for example:
| Service Tier | Price per Word (EUR) | Key Features |
| Basic | From €0.05 | Basic contentmachine-aided translationprofessional proofreading2 revisionsPM support24/7 updates |
| Business | €0.08 – €0.13 | Manual professional translationhigh-quality publication-readyproofreading & editingPM support |
| Pro | €0.10 – €0.16 | Expert native translationcontextual & substantive editingunlimited revisionsPM support |
| Custom | Contact for pricing | Tailored solutions for scientific/technical content and bespoke requirements |
Per-Page and Project-Based Website Translation Pricing
For smaller websites or specific, discrete projects, per-page or project-based pricing simplifies budgeting.
A vendor quotes a flat fee to translate your entire website. No surprises.
This model works for static brochure sites, landing page campaigns, or limited-scope projects. It’s popular with startups and small businesses lacking visibility into exact word counts.
The risk is scope creep. If you underestimate page count or discover dynamic content after committing, you’re either charged extra or the quality suffers. Vendors build safety buffers into project pricing, increasing the per-unit cost to account for uncertainty.
Subscription and Retainer Pricing for Multilingual Websites
Enterprises with continuous translation adopt subscription models. Rather than project-by-project negotiation, teams pay monthly retainers covering allotted translation volume.
This model incentivizes vendor investment in your account. They staff permanent linguists or allocate priority capacity, knowing you’re a consistent revenue stream. Turnaround times improve. Quality becomes predictable. Integration deepens.
Retainer pricing suits SaaS platforms releasing new features monthly, ecommerce companies with continuous product uploads, and publishing platforms with weekly content updates.
The cost is higher per-word this way, but the benefit is reliability and speed. A monthly retainer transforms translation from a procurement bottleneck into a predictable business process.
What Is the Cost of Multilingual Website Maintenance?
Localization is not a one-time event. It’s an ongoing operational expense.
Launch costs are just the beginning. After your translated website goes live, the real work starts: product updates, seasonal content, compliance changes, marketing campaigns, UI adjustments, security patches affecting language strings, and competitive feature additions. Each modification triggers a translation update.
Ongoing Content Updates and Release Cycles
Agile localization requires workflow redesign. Instead of batching all translation work quarterly, you integrate continuous translation into sprint cycles. Content strings are extracted and submitted to translation as features complete, not when the entire release is done.
Translation management systems enable this velocity. Content changes trigger automated translation requests. Linguists work on discrete, smaller chunks rather than massive batches. Approval workflows accelerate. Releases ship on schedule across all markets.
SEO Localization and Multilingual Optimization Costs
SEO localization converts markets. It researches search demand, user behavior, and competitive keywords in each market language, then rewrites content to rank for local keywords while maintaining brand voice consistency.
This is a distinct service layer beyond translation.
Expect to budget 30–50% additional cost on top of base translation for serious SEO localization. A $20,000 translation project becomes $26,000–30,000 with proper SEO localization.
Human vs. Machine Website Translation: Cost vs. Accuracy

The emergence of large language models (LLMs) and neural machine translation (NMT) systems has fundamentally altered translation cost economics.
Machine translation, powered by systems like Google Translate or specialized neural engines, costs virtually nothing to operate at scale. Translating 1 million words costs the same as translating 100 words. This is transformative for high-volume, low-risk content.
But machine translation isn’t perfect. It hallucinates context, translates idioms literally, and sometimes reverses meaning. For some content, post-editing by human linguists is mandatory.
When Machine Translation Reduces Website Translation Cost
Machine translation excels for high-volume, low-consequence content. E-commerce product catalogs, internal documentation, FAQ repositories, and data-heavy content are ideal candidates.
Consider an online retailer with 50,000 product descriptions. Machine translation processes all 50,000 in hours, at near-zero marginal cost. A human translator would require months and cost $15,000–25,000. With MTPE, a linguist reviews machine-generated translations, fixing errors. The entire project gets completed in 2 weeks for a third of the price.
The economic model is: machine translates cheaply; human post-edits selectively; quality reaches an acceptable threshold for internal or lower-stakes audiences.
When Human Translation Is Mandatory for Business Sites
High-risk, brand-critical, or legally regulated content demands human translation with minimal machine assistance.
Your website’s homepage, core landing pages, and checkout flows are brand-defining experiences. A machine mistranslation here damages credibility permanently.
Legal and compliance pages, Patent translation, regulatory documentation, terms of service, and privacy policies, Financial services, healthcare content, sales pages and pitch materials are also non-negotiable. must be certified accurate. A mistranslation in legal terms can expose your company to liability. Human legal translators with domain expertise are essential. The necessity outweighs the extra cost by a large margin.
Real-World Website Translation Cost Examples
Pricing varies dramatically across business models. These scenarios illustrate realistic cost structures without hard guarantees.
Small Business and Startup Website Translation
A startup SaaS company with 30 pages, 25,000 words, launching in 3 European markets (French, German, Dutch) needs initial translation plus quarterly updates.
Initial translation: 25,000 words × 3 languages = 75,000 source words Per-word rate: 12¢ (modest volume discount) Translation cost: $9,000
CMS integration (if needed): $2,000 Project management and QA: $1,500
Subtotal: $12,500
Quarterly maintenance: Assume 3,000 new words per quarter × 3 languages × 12¢ = $1,080 quarterly = $4,320 annually
Year 1 total: $12,500 + $4,320 = $16,820
This budget is reasonable for a lean startup that can afford professional translation without breaking early-stage cash burn constraints.
Enterprise Website Translation Cost Drivers
A large enterprise with 400 pages, 500,000 words, translating into 12 languages, with SEO localization and ongoing monthly updates, requires industrial-scale infrastructure.
Initial translation: 500,000 words × 12 languages = 6,000,000 source words. Per-word rate: 9¢ (aggressive volume discount for enterprise scale) Translation cost: $540,000
SEO localization (30% uplift): +$162,000
CMS integration and TMS setup: $35,000
Project management, QA, governance: $50,000
Subtotal: $787,000
Monthly maintenance: Assume 15,000 new source words monthly × 12 languages × 9¢ = $16,200 monthly Annual maintenance: $194,400
Total infrastructure (TMS, automation, vendor management): $50,000 annually
Year 1 enterprise total: $787,000 + $194,400 + $50,000 = $1,031,400
Year 2+ (no launch cost): $244,400
This reflects real enterprise localization programs. Large organizations often allocate 0.5–1 FTE internally for localization management, adding $60,000–120,000 in labor.
How to Estimate and Control Website Translation Cost
Procurement teams can optimize translation spend without sacrificing quality.
What Information Vendors Need to Quote Accurately
Getting an accurate quote requires providing vendors with clear scoping information:
- CMS details
- Content audit
- Language scope
- Update cadence
- SEO requirements
- Quality standards
- Timeline
- Current assets
Cost Optimization Best Practices for Multilingual Websites
Smart organizations reduce translation cost without compromising quality.
Reuse and modularization of the content leverages translation memory, cutting cost 20–30%. Structured CMS architecture is easier to extract, translate, and reintegrate. This drives cost down. Centralized glossary management reduces per-word cost drops because translators don’t second-guess terminology.
Negotiating with 12 different translation vendors for 12 languages is inefficient. A partner like Circle Translations, supporting 120+ languages, provides consolidated billing, consistent quality, and volume discounts.
Lastly, don’t translate everything simultaneously. Launch core markets and content first. Expand languages and content depth over time. This spreads cost and lets you iterate localization strategy based on early market feedback.
Why Professional Website Translation Services Cost More But Pay Off
Budget-conscious procurement teams sometimes view professional translation costs as an expense to minimize. But professional localization is an investment in market entry quality and brand integrity.
A professional translation service drives ROI with immaculate user experience. Customers notice clunky phrasing. Competitors in that market rank higher for relevant keywords. Conversion rates lag English-language performance.
Circle Translations delivers:
- Native-speaker expertise with 120+ languages
- Industry specialization
- Consistency across scale
- Reduced rework
- SEO performance
- Compliance and risk mitigation
Website Translation Cost — FAQs
How Much Does It Cost to Translate a Business Website?
At Circle Translations, we typically see small business websites (around 25,000 words across three languages) fall in the $8,000–$15,000 range for initial translation, while enterprise-scale sites (500,000+ words across 12 languages) with SEO-focused localization often range from $500,000 to $1M+ at launch. As multilingual programs mature, organizations usually allocate 20–30% of their annual marketing budget to ongoing localization. Final costs depend on scope, so accurate estimates require clarity on content volume, language count, CMS platform, and quality standards.
Is Website Translation Priced Per Word or Per Project?
Most localization providers use per-word pricing for content, combined with project or monthly fees for engineering, CMS setup, and ongoing maintenance. For ongoing needs, enterprise clients often choose monthly retainers that bundle translation, infrastructure, and vendor management into a predictable cost model.
At Circle Translations, per-word pricing typically ranges from €0.08 to €0.16, depending on language pair, volume, and technical complexity. Project or flat fees may apply for CMS integration, localization engineering, QA, and onboarding.
What Is the Cost Difference Between Website Translation and Website Localization?
Website translation converts words; website localization converts markets.
Translation is linguistic, whereas localization includes translation plus SEO optimization, UX adjustments for regional preferences, formatting changes (number formats, currency, measurements), cultural adaptation, and market-specific content modifications.
Website localization cost typically runs 30–50% higher than basic translation.
Does Translating a CMS-Based Website Cost More?
Yes, significantly. CMS websites often require connectors, string handling, staging workflows, and ongoing synchronization, all of which add to the overall translation cost.
A static HTML website requires simple file translation. A CMS-powered site requires integration. WordPress needs plugin setup and testing. Shopify requires custom app configuration or TMS integration. Webflow requires collection duplication and localization setup. Custom or headless CMS platforms require API integration and developer involvement.
How Much Does Multilingual Website Maintenance Cost Per Month?
Ongoing localization costs vary by how often content changes, how many languages you support, and your approval process. A static brochure site may spend $500–1,000 per month, while a SaaS product with weekly releases can reach $5,000–15,000, and ecommerce sites with daily updates often budget $10,000–30,000 monthly. Many enterprises use retainers to keep costs predictable, but the biggest cost driver is content velocity.
Is Machine Translation Cheaper for Websites?
Machine translation can reduce cost for high-volume, low-risk content, but still requires human review for public-facing business pages to maintain quality.
However, machine translation fails for brand-critical content. Your homepage, core landing pages, checkout flows, and legal pages must be human-translated. Sophisticated localization strategies use a hybrid approach: machine translation + post-editing for high-volume, low-stakes content; pure human translation for brand-critical and regulated content. This balances cost efficiency with quality requirements.
Conclusion
Website translation cost is a strategic investment in market expansion, customer experience, and international revenue growth.
You have to budget with content volume and complexity, language pair tier, CMS architecture, maintenance cadence, and quality depth in mind.
Professional translation cost directly influences market success. A well-translated, SEO-optimized website in a target market generates qualified leads, builds trust, and drives conversion.
As a B2B decision-maker, you’re weighing translation cost against revenue impact. The companies winning international markets are those who invest in professional, continuous localization as a core go-to-market capability.
Circle Translations provides the consistency, quality, and scale that growing businesses require. Whether you’re translating your first website or managing localization for a global platform, understanding website translation cost puts you in control of a critical business process.
Your next market awaits. Make sure it’s translated right with Circle Translations.
















