A single mistranslated claim in a multi-billion-dollar patent dispute is not just a linguistic error. It is a strategic liability. In the high-stakes world of Intellectual Property (IP), the translated document is the ground upon which the battle is fought. Whether you are navigating an infringement case in the newly formed Unified Patent Court (UPC), an invalidation proceeding in Tokyo, or the complex discovery phase of a U.S. district court case, the precision of your evidence determines the strength of your argument.
IP litigation translation is a high-precision service used in legal disputes. It involves translating patents, technical evidence, and court documents into another language without changing their legal meaning. Accuracy is critical because these documents may be reviewed by judges, arbitrators, or opposing counsel.
At Circle Translations, we provide specialized IP litigation translation services. Our work ensures your technical evidence is clear, neutral, and court-ready. We support cases in more than 120 languages while meeting strict legal and compliance standards.
What is IP Litigation Translation
Many law firms assume that a general legal translator can handle an IP dispute. This is a risky misconception. IP litigation translation is a distinct discipline that sits at the intersection of complex technology and specialized law.
How is it different from standard legal translation?
Standard legal translation handles contracts, corporate bylaws, and general business correspondence. IP litigation translation handles the “contentious” phase. It requires a significantly higher accuracy threshold because the documents will be scrutinized by opposing counsel, technical experts, and judges looking for any inconsistency to exploit.
The primary differences include:
- Stricter Accuracy Thresholds: In litigation, a translation must capture the “legal intent” of a claim, not just the general meaning.
- Chain-of-Custody (CoC): For evidence to be admissible, there must be a documented “paper trail” showing who handled the file, ensuring it hasn’t been tampered with.
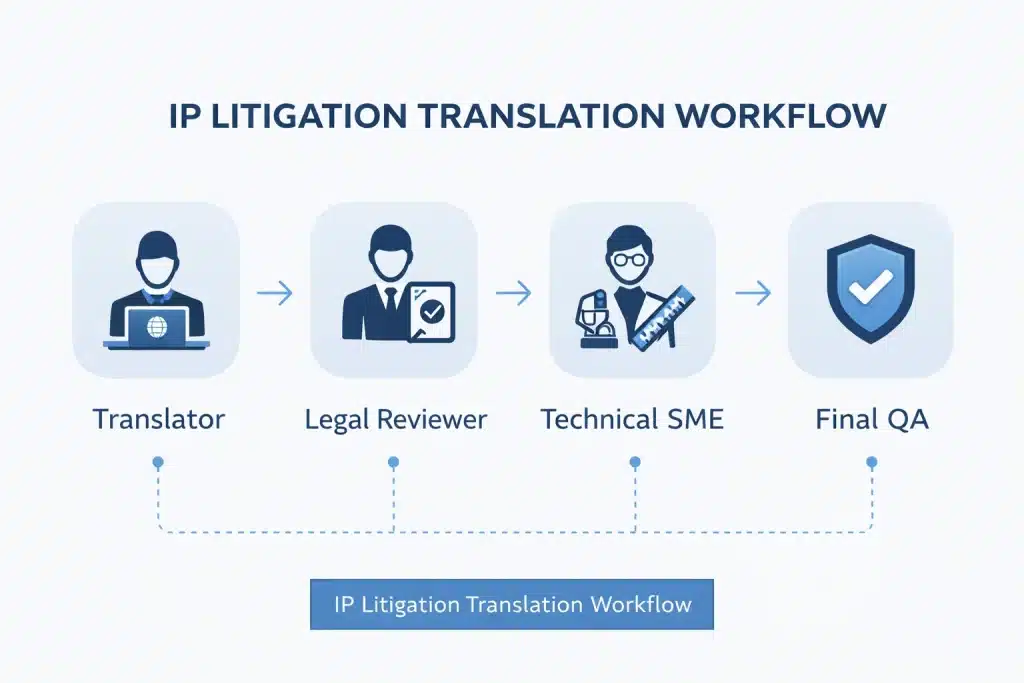
- Multi-Stakeholder Review: It is a standard process to have one editor. IP litigation needs to maintain at least these four-step process:
– Translator
– Legal Reviewer
– Technical Subject Matter Expert (SME)
– Final Legal QA. - Certification Standards: While a contract might be signed, litigation documents often require sworn/certified status, or even notarization, to meet specific jurisdictional rules (such as USPTO or EPO standards).
Major industry players like RWS and Park IP (a Welocalize company) have set the benchmark for this by creating “litigation-specific” quality layers. For instance, Park IP integrates its translation workflow directly into e-discovery platforms like Relativity to maintain a seamless, secure audit trail.
Where do errors in litigation translations cause risk?
In a high-stakes IP dispute, a translation error is more than a typo. It is a crack in your legal foundation. According to recent 2026 industry surveys, nearly 42% of legal professionals have encountered significant problems due to inaccurate translations, ranging from minor procedural delays to the complete loss of intellectual property rights.
When a document enters the courtroom, it is scrutinized by opposing counsel looking for “daylight,” any small gap in meaning they can use to challenge your case. Here are the five highest-risk areas where translation errors most often occur:
- The “Property Lines” of your Invention: Think of a patent like a fence around your house. If the translation uses the wrong word for “boundary,” your fence might move. Suddenly, a competitor might be able to build on your “land” because your translated document didn’t clearly state where your invention starts and ends.
- Proof of “Who Had it First”: To win a case, you often have to show that your idea was original. If you translate an old technical manual poorly, you might fail to prove that your idea was actually first. If the judge can’t understand the proof, they might cancel your patent.
- Technical Names: Every industry has its own “slang.” If a translator isn’t an expert in your specific field (like chemistry or software), they might use a common word for a very specific part. This makes your evidence look confusing or unprofessional to the judge.
- The “Paper Trail”: For a document to be used in court, the judge needs to know exactly who handled it from the moment it was found. If the translation of this “tracking log” is messy, the other side might argue that the document was tampered with, and the judge might throw it out.
- Witness Stories: Even a small translation mistake can make an honest person look unreliable on the witness stand.
The Consequences: Why Precision is Non-Negotiable
The fallout from these errors isn’t just linguistic, it’s financial and procedural. In one landmark case, a mistranslated clause in a Spanish-to-English arbitration contributed to a $1.76 billion judgment.
The typical “domino effect” of a translation error includes:
| Consequence | Legal Impact | Business Reality |
| Case Delays | Courts may order re-translations or stay proceedings until accuracy is verified. | Legal fees escalate and product launches are postponed. |
| Evidentiary Rejection | The judge strikes the document from the record entirely (the “death blow” to a piece of evidence). | Your primary proof of infringement or prior art vanishes. |
| Weakened Arguments | Your legal strategy is forced into a defensive posture, defending the translation instead of the case. | Settlement leverage decreases, often forcing an unfavorable deal. |
| Jurisdictional Non-Compliance | Failure to meet local “sworn” or “certified” standards leads to immediate filing rejection. | Missing a court-mandated deadline can result in a default judgment. |
Why do international IP litigation cases require specialized linguists?
International IP disputes require a “triple-threat” linguist: someone who is a native speaker, a legal expert, and a technical subject-matter specialist. You cannot translate what you do not understand.
If a case involves a CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing patent, the translator must understand both the patent laws of the local jurisdiction and the molecular biology of the science. Competitors in this space, such as RWS or Park IP, emphasize this subject-matter approach because it reduces the risk of technical nuances being “lost in translation.” We follow this same principle. We match your case with a linguist who holds a degree or has significant experience in the specific field of the dispute, be it semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, or aerospace engineering.
What documents typically require translation in cross-border IP litigation?
IP cases are notoriously document-heavy. The volume of data unearthed during the discovery phase alone can reach millions of pages. We typically categorize these into several tiers of importance:
1. The Core Patent Bundle
- Patent Claims & Specifications: The “heart” of the case.
- Prior Art: Foreign-language journals, older patents, and technical manuals used to challenge validity.
- File Histories (Wrapper): The back-and-forth correspondence with patent offices during the grant process.
2. Evidentiary & Discovery Materials
- Lab Notebooks and R&D Records: Often handwritten or containing highly technical jargon.
- Internal Corporate Emails: Requiring a balance of technical understanding and cultural nuance to capture intent.
- Marketing & Sales Materials: Used to prove “commercial success” or “willful infringement.”
3. Court and Administrative Documents
- Pleadings & Motions: Official documents filed with the court.
- Expert Reports: Deeply technical documents written by scientists or professors that must be translated with 100% terminological consistency.
- Deposition Transcripts: Real-time records of witness testimony.
Do courts require certified or sworn translations?
In simple terms, yes. If you are bringing a document to court that isn’t in the official language of that country, the judge usually won’t even look at it unless it has a “badge of trust” attached.
Here is the simple breakdown of what those badges are and where they are used.
The 4 Types of “Official” Translations
Think of these as levels of proof. The more serious the court case, the higher the level of proof you need.
- Certified Translation: This is the most common. It’s a standard translation with a signed letter (a “Certificate of Accuracy”) from the translator. It’s their way of saying, “I promise this is a true and correct copy.”
- Sworn Translation: This is a step up. In many countries, translators must take an official oath before a court or the government. They have a special stamp. When they “swear” a translation, it carries the weight of the government’s approval.
- Notarized Translation: This has nothing to do with the translation’s quality. A Notary Public simply checks the translator’s ID and watches them sign the paper. It proves that the person who signed the certificate is a real person.
- Apostille: This is for international travel. It’s an official government sticker that proves the Notary’s signature is real. It’s used when you take a document from one country (like the US) to another (like China).
Here is a Breakdown by Region
Different patent offices and courts have different “house rules.”
| Region / Body | What they usually want | Why? |
| USPTO (USA) | Certified | They trust a signed “Statement of Accuracy” from a professional agency. |
| EPO (Europe) | Certified | Documents must be in English, French, or German. They require a professional certification to ensure technical words match. |
| CNIPA (China) | Notarized & Apostille | China is very strict. Evidence from outside China almost always needs a Notary’s stamp and an international “Apostille” sticker. |
| JPO (Japan) | Certified / Formal | Accuracy is everything in Japan. They require formal certifications, and if the translation is bad, they can throw the case out. |
Litigation translation workflow: how do we maintain accuracy, neutrality, and legal defensibility?
To make sure your case is built on a solid foundation, we don’t just translate your words, we protect your evidence. At Circle Translations, we use what experts call a “defensible” workflow. This is a specialized, multi-step process designed to ensure that if a judge ever asks, “How do I know this translation is right?” you have a perfect, documented answer. This approach (similar to the high standards used by industry leaders like RWS) ensures your evidence is “bulletproof” against challenges from the opposing side.
Here is exactly how we handle your documents from the moment you hand them to us until they are ready for the judge’s desk:
1. We start with a “Digital Vault” (Secure Upload)
Your documents are your company’s “crown jewels.” We don’t let them sit in a regular email inbox. You begin by uploading your files to our Secure Portal. This is an encrypted environment that creates a permanent record of who accessed the file and when. This “paper trail” is vital for showing the court that your evidence was handled safely.
2. Strategic Resource Allocation (Domain-Specialized Translators)
To ensure absolute technical accuracy, we assign your case to a linguist with deep “Subject Matter Expertise” (SME) in your specific technology sector, whether that is telecommunications, biotechnology, or semiconductor manufacturing.
These professionals do not just speak the language; they understand the technical nuances and the “Patentese” (the highly formalized language of patent law) required for the case.
3. We perform a Legal Logic Check (Legal Reviewer)
Once the first draft is ready, our legal specialists step in. They aren’t just looking for typos; they are making sure the document “sounds” like a legal filing. They verify that the tone is professional and that the legal meaning matches the specific rules of the country where you are fighting the case.
4. We bring in the Scientists (Technical SME Review)
For very complex inventions, like a new software code or a chemical formula, we involve a Subject Matter Expert (SME). This is often a scientist or engineer who checks the technical facts. They ensure that your invention is described correctly so that the judge or the jury isn’t confused by technical errors.
5. We conduct a Final “Court-Ready” Check (Legal QA)
Before anything reaches you, our quality team performs a final sweep. We check the small but critical details that law firms often worry about: Are the page numbers identical to the original? Are the stamps and signatures in the right place? Are the dates 100% correct? We do this so you can file the document immediately without having to double-check our work.
6. We provide the “Badge of Trust” (Sworn/Certified Output)
Finally, we deliver your “court-ready” package. If the jurisdiction requires it, we provide a Certified or Sworn version of the document. This is our official, legal promise to the court that the translation is a true and honest copy of the original.
Why we do it this way
In international law, the other side will look for any excuse to get your evidence thrown out. By following this strict 6-step process, we take that weapon away from them. When we handle your translations, we move the conversation away from “is this word right?” to “the process was perfect.” This gives your legal team the confidence to focus on winning the case, while we handle the linguistic heavy lifting.
Who is involved in IP litigation translations? (Roles & Responsibilities)
In a high-stakes IP case, a single person cannot handle the entire translation process. It takes a coordinated “army” of specialists to ensure your evidence is ready for court. When we handle your case, we assemble a dedicated team where every member has a specific, critical role.
We have,
- Lead Linguist: The primary translator responsible for the initial draft.
- Legal Reviewer: Ensures the translation meets the specific stylistic and formal requirements of the court.
- Technical SME: A scientist or engineer who verifies that the “invention” is described accurately.
- Litigation Project Manager: Your single point of contact who manages deadlines, budgets, and secure delivery.
- Formatting/DTP Engineer: Ensures that complex diagrams, chemical formulas, and tables are perfectly replicated in the target language.
What security standards do litigation translations require?
In IP litigation, the documents being translated are often the “crown jewels” of a corporation. We treat them as such. Our security protocols include:
- Strict NDAs: All linguists and staff are under binding non-disclosure agreements.
- ISO 27001 & GDPR Compliance: We follow international standards for data protection and privacy.
- Encrypted Portals: We never send sensitive documents via unencrypted email. All transfers happen through secure, bank-grade portals.
- Access Control: We apply the “principle of least privilege”; only the linguists directly working on your case can access the files.
How long does IP litigation translation take, and what affects the timeline?
In the legal world, a deadline is not a suggestion; it is a hard wall. We provide realistic timelines based on the volume and complexity of the case.
- Standard Turnaround: 2,000–2,500 words per business day is the industry standard for high-quality human translation.
- Expedited/Rush: For emergency filings or overnight discovery needs, we can mobilize teams of linguists to handle 10,000+ words per day through parallel processing.
- Rolling Delivery: For massive eDiscovery sets, we deliver documents in batches so your legal team can start their review while the rest of the project is being completed.
What affects turnaround speed in litigation translation?
In IP litigation, “fast” must be balanced with “accurate.” While we offer rush services, several factors dictate the timeline for a court-ready document:
- Technical Complexity: A simple contract is quick. A patent for a biotech drug or a semiconductor requires deep research and technical double-checks that take more time.
- Density of Evidence: Thousands of pages of “discovery” materials, like handwritten lab notes or internal emails, are more time-consuming to process than a standard filing.
- Multiple Reviewers: In large cases, your lead counsel, technical experts, and foreign legal teams all need to approve the draft. More “cooks in the kitchen” means a longer sign-off process.
- Certification Needs: Getting a document “sworn” or notarized involves administrative steps, like physical stamps or notary appointments, which can add 24–48 hours.
- Foreign Counsel Approval: Local lawyers in the country where you are filing often want to verify that the translation matches their specific procedural rules.
- Complex Formatting (DTP): If your evidence includes blueprints, flowcharts, or chemical formulas, our engineers must recreate these visuals so the judge sees a mirror image of the original.
How pricing works for IP litigation translation services
Pricing for litigation is different from a standard patent filing. While a filing is routine, litigation documents are legal evidence. They require extra layers of review to ensure they stand up in court.
To keep your budget predictable, we use four simple models:
- Per-Word (The Standard): Best for technical patents and witness statements. This is the most transparent way to pay. The rate reflects a “triple-check” process: a translator, a legal reviewer, and a technical expert all review the work.
- Per-Page (Sworn/Official): Best for short documents like certificates or stamps. This flat fee covers the translation, the formatting, and the official court stamp.
- Per-Hour (Expert Review): Sometimes you don’t need a full translation. You can hire our experts by the hour to help your lawyers “skim” documents or explain a specific technical diagram.
- Project-Based (Large Evidence Sets): If you have thousands of pages of emails or notes, we create a custom bundle. We often use a “search and translate” approach to find the most important files first, so you don’t have to translate unnecessary data.
Which factors influence cost the most?
When budgeting for an international case, it is important to remember that not all documents are created equal. These six factors have the biggest impact on your final quote:
- Technical Complexity: High-tech fields like biotechnology or semiconductors require specialists with advanced degrees. These experts charge higher rates than generalists.
- Legal Depth: Core evidence (like patent claims) requires more “legal logic” checks. Higher risk means more experts are involved to ensure the document is “bulletproof.”
- Volume of Exhibits: Managing hundreds of small files, like emails or lab notes, requires more administrative work than translating one long, continuous document.
- Certification Levels: Standard translations are the most affordable. “Sworn” or “Notarized” versions (often required in Europe or Asia) include extra government or administrative fees.
- Formatting (DTP): If your evidence includes blueprints, flowcharts, or handwritten notes, our engineers must manually recreate them to match the original layout.
- Delivery Speed: Court deadlines are non-negotiable. If you need a massive document set translated over a weekend, “rush” services involve 24/7 team coordination and carry a premium.
Why choose us for IP litigation translations (B2B value proposition)
When you choose Circle Translations, you are not just buying a translation; you are buying peace of mind. We provide:
- Litigation-Qualified Linguists: Our team understands the nuances of cross-examination and evidentiary rules.
- 120+ Languages: We provide a single point of contact for global disputes, whether they are in Germany, China, Brazil, or the US.
- Court-Ready Accuracy: Our documents are formatted and certified to be filed the moment they land in your inbox.
- Secure Infrastructure: We provide the high-level security that corporate counsel and top-tier law firms demand.
How we support law firms and corporate counsel
We act as an extension of your litigation team, providing the technical and linguistic support needed to win complex cases. Here is how we collaborate with your attorneys:
- Joint Glossaries: We build a “master list” of terms with your team. This ensures every technical word stays consistent across every motion, report, and deposition.
- Pre-Trial Alignment: We meet with your counsel to understand your strategy. This helps our linguists focus on the specific nuances that matter most to your argument.
- Urgent Filings: Litigation is unpredictable. We provide 24/7 “rapid response” teams to handle last-minute court orders or surprise motions overnight.
- Parallel Processing: If you are fighting in multiple countries (e.g., the US, Germany, and China), we manage all languages at once to keep your arguments identical across borders.
- Encrypted Communication: We eliminate leak risks by using bank-grade secure portals for all document exchanges and discussions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes IP litigation translation different from standard translation?
Litigation translation requires a higher level of “legal defensibility.” It is not just about the gist; it is about ensuring the technical scope and legal intent are preserved for use as evidence in court.
Do international courts require certified or sworn translations?
Yes, in almost all cases. The specific type of certification (sworn, notarized, or agency-certified) depends on the rules of the local court or patent office (e.g., EPO, USPTO, CNIPA).
Which documents need translation for IP litigation cases?
This typically includes patent claims, prior art, expert reports, witness depositions, internal R&D correspondence, and official court motions.
How fast can litigation translations be delivered?
We offer expedited tiers, including overnight and weekend support for urgent filings. For very large projects, we use rolling delivery to keep your case moving.
How do you maintain accuracy in high-stakes IP disputes?
We use a multi-layer QA process: a domain-specialized translator, a second legal reviewer, and a technical SME, all working against a unified case glossary.
How much do IP litigation translation services cost?
Pricing is usually based on the volume of words, the technical complexity, and the level of certification required. We provide transparent, project-based quotes to help you manage your litigation budget.
How do you protect confidential litigation documents?
We use encrypted portals, strict NDAs, and ISO-compliant workflows to ensure that your sensitive IP evidence is never compromised.